You travel thousands of miles to experience new cultures. So why would you settle for a generic hotel or nondescript tourist restaurant? The burgeoning peer-to-peer or sharing-economy movement allows travelers to skip the traditional booking options and live la vita local by staying in other people’s homes, driving their cars, eating in their kitchens, and otherwise, seeing a new destination through their eyes.
Why share? After the economic downturn, people developed innovative ways to make money by sharing resources they already had, such as houses, vehicles, and skills, creating a new economy based on collaborative consumption. While this power-to-the-people movement has mobilized an army of microentrepreneurs, it has also resulted in traveler benefits ranging from practical (savings, convenience, and personalized attention) to enriching (authentic experiences and real human connection). It also supports local communities and encourages sustainability.
A travel style favored by generations of backpackers, peer-to-peer has grown meteorically and become more accessible in recent years through the use of the Internet and social media, both of which help connect travelers with hosts and services.
Here are some of the more popular ways to travel in today’s sharing economy, from house swapping to unique tours guided by locals.
Share a House
 |
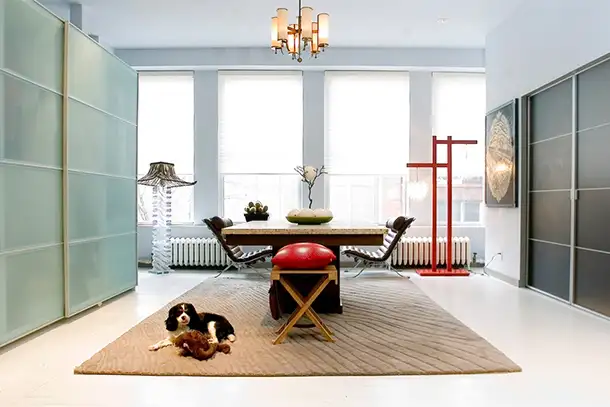 |
From crashing on a stranger’s couch to sleeping in a luxurious penthouse suite, the trend of staying in alternative accommodations such as apartments, villas, or even single rooms in private homes has exploded over the past few years, mainly thanks to Airbnb, an online community marketplace for homeowners and travelers that debuted in 2008.
The site grew quickly via word of mouth, attracting people who liked the local experiences it provided. According to Airbnb, “When you stay in an Airbnb [property], you have the opportunity to learn from a local. Airbnb hosts can give you insider knowledge you couldn’t find elsewhere. Hosts have a ton of local pride and are generally eager to share their tips with you to make your trip even more amazing.”
While Airbnb has recently hit the mainstream, the concept of home sharing is not new. Started as a pre-Internet business in 1992, HomeExchange, a house-swapping service popularized by the movie The Holiday, has been connecting traveling homeowners for decades. Nevertheless, the company, which offers free accommodations via a true one-to-one home swap, has received a boost from the current sharing-economy movement.
According to Ed Kushins, founder and president of the company, “Collaborative consumption is turning things that used to be private into something that can be used or rented. Sharing is still a transaction, but with HomeExchange, there is no money changing hands and you get your house back. It’s like having a guest in your house.”
Staying in someone’s home—as opposed to booking a hotel—can make a vacation more affordable and add convenience, both in terms of perks and personal interactions. Kushins says, “You can save on food bills by not eating at a restaurant for every meal, and there are no early check-in or checkout rules; plus you get personal instructions and accommodations and get to meet people, often friends of the exchange partner.”
A bevy of similar websites offer lodging options varying from free to paid and simple to luxurious. Travelers can crash and see the town with a local through Couchsurfing or pitch a tent in someone’s yard with Campinmygarden.com. Airbnb competitor Roomorama has listings for short-term rentals, and the like-minded FlatClub leverages social media “clubs” to create an additional layer of trust. Onefinestay focuses on a curated listing of more upscale homes.
Share a Ride
Once you’ve booked a stay in a stranger’s home, the next natural step into the peer-to-peer world is driving a stranger’s car, which has appeal for travelers wanting to save money and get more personalized service when they hit the road.
Typically, car sharing involves renting cars for short periods of time, often by the hour. An alternative to car ownership, this helps keep unnecessary vehicles off the road, thus making things a little easier on the environment. In recent years, it has expanded to fulfill the longer-term needs of travelers, who can rent directly from car owners (often other travelers who have parked at the airport) on a daily basis, making use of underutilized vehicles and avoiding the hassles associated with traditional car rentals.
RelayRides, a car-sharing marketplace focused on U.S. airports, started out emulating the Zipcar model with on-demand, hourly car rentals, but found that it was more competitive with traditional car-rental companies such as Hertz and Avis.
According to Steven Webb, RelayRides’ Director of Community and Communications, “[Our customers] were people who already had cars but wanted them for specialty purposes [like travel] and would like something more convenient and affordable than traditional rentals.”
Webb claims that car sharing saves travelers up to 40 percent and provides them with the added benefits of choosing their car and getting picked up at the airport by the owner (rather than waiting in a long line and getting whatever happens to be in the lot at that moment). In other words, if you choose a red 2014 Toyota Prius from the site’s listing, you’ll get to drive that exact same red 2014 Toyota Prius.
Another option, FlightCar, allows prescreened drivers to rent from people who have parked their cars at the airport. Owners get free airport parking, a car wash, and payment if their car is rented out, and renters receive low rates and free curbside pickup and drop-off at Boston, Los Angeles, and San Francisco airports. There’s no waiting in line, no paperwork, and none of the hidden ancillary fees that have been plaguing car renters for years.
Similar services include Hubber, Getaround, and JustShareIt, which offers cars plus motorcycles and other vehicles.
Taxi alternatives Uber, Lyft (you’ve probably seen the fuzzy pink mustaches adhered to bumpers), and Sidecar provide on-demand ride sharing via smartphone apps. Spinlister offers sharing options for bicycles (as well as skis and snowboards). And if you want to set sail, GetMyBoat will help you find the perfect vessel.
Share a Meal
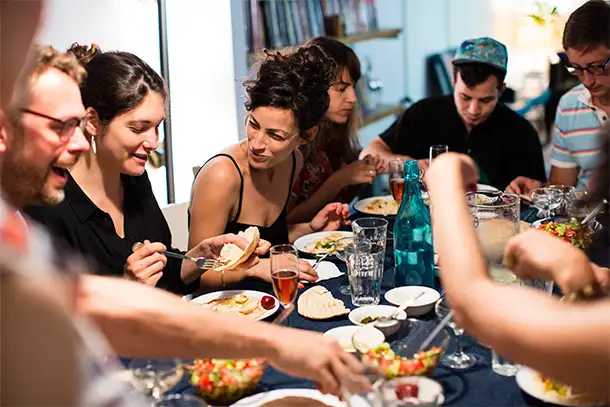 |
 |
Houses and vehicles aren’t the only things up for collaborative consumption. People are craving authentic experiences through food. And plenty of new websites are making it easier to connect passionate chefs—and grandmothers—with hungry travelers who want to share home-cooked meals with locals in just about any destination around the world.
These social dining sites—through which you can book meals or cooking classes in someone’s private kitchen—fill the need of an ever-growing niche of travelers who have become dissatisfied with generic food options available at resorts and tourist restaurants and want more memorable meals that reflect the local culture. They are more immersive and offer personalization, since hosts often build meals around specific dietary preferences (e.g., a four-course vegetarian dinner in Naples, Italy) or even tailor set menus to suit individual needs.
Noah Karesh cofounded Feastly in 2013 to help people “understand local culture and connect.” He says, “It’s a vehicle to sustain relationships and provide meaningful interaction around food. … Meal options range from $5 mac and cheese to $100 multicourse meals and can accommodate all dietary lifestyles.” Currently, the site offers experiences in New York, Washington, D.C., and San Francisco as well as a number of other U.S. cities.
EatWith, a site with a similar mission, launched a year ago and has a presence in more than 30 countries. According to Marketing Director Katie Sorene, the two cofounders were disappointed in tourist restaurants in Greece, where they didn’t learn anything about Greek culture; they found that having dinner in peoples’ homes was the best experience. She says, “It’s more personal and is incomparable to going to restaurants since hosts invite friends and other travelers. It appeals to travelers who are interested in culture and want to taste local food and meet people.”
EatWithaLocal, Meal Sharing, and Cookening also offer social dining options in multiple cities, and Home Food focuses on Italy.
Share an Experience
A street-art walk in Brooklyn, a tour of Paris from the back of a 1975 Vespa, and even a fishing trip with a Fijian king: When it comes to seeing a destination, websites like Vayable are helping travelers find unique experiences tailored to specific interests by connecting them to vetted local guides.
According to founder Jamie Wong, “Travelers benefit by building connections with locals, which comes to define the trip.” These tours also bring people into new neighborhoods, away from the typical tourist spots and cookie-cutter activities.
But sharing an experience can benefit more than the traveler. Wong says, “The money gives back to local communities. Economic distribution helps empower individuals to support themselves and reroutes capital into pockets of individuals.”
Wong created Vayable out of what she recognized as a collective longing for authentic experiences. She says, “The 2008 economic crash gave birth to a need for human connection and experiential travel. People found that money doesn’t make them happy. Experiences do.” Started in 2011 in San Francisco, the website has blossomed in the past three years to include 600 destinations around the world.
CanaryHop, a marketplace for activities and tours, and online community GuidedByALocal offer more options for connecting travelers with local experiences.
Trust and Safety in the Sharing Economy
The potential for sharing resources, human connection, and cultural exchange may be appealing, but many travelers are left with a simple question: Is peer-to-peer travel safe?
Many of these websites and apps do the initial vetting for you. So while you are still essentially interacting with strangers, there are many checks and balances along the way that help build trust and allow you to make informed decisions.
For example, most of these services use multilayered vetting systems that include verifying identities through credit cards, phone numbers, social media accounts, etc. You can also read through profiles and verified reviews or check references of a given host.
RelayRides uses a two-way review system, in which car owners rate drivers and vice versa. The company also checks driving records and offers an insurance product for renters that includes liability and collision as well as roadside assistance and customer support.
Some sites have built-in functionalities for direct messaging between guests and hosts, which allows them to get to know each other while protecting their personal identities. According to Kushins, “By the time you agree to the exchange, the fear has gone away. You get to see and learn about the person, and the natural apprehension you have dissipates.”
Meal-sharing businesses like EatWith and Feastly follow federal or local food-safety regulations. Both sites also have systems in place to verify chefs, either through tools like Skype or by sending “ambassadors” to test out the food and overall dining experience.
The Future of Peer-to-Peer Travel
While the sharing economy defies the status quo set by traditional business models, it’s facing its share of challenges over legitimacy and perceived competition.
For example, Airbnb is currently in legal battles with New York for listing “illegal” apartment rentals and for costing the state millions in hotel tax dollars. San Francisco airport sued FlightCar for skirting the airport fees that traditional car-rental agencies pay. And, according to Reuters, Seattle just voted to limit the expansion of ride-share companies like Uber, Lyft, and Sidecar and require that drivers and cars meet the same insurance standards as taxis.
Despite the rules imposed by regulatory bodies and competition-fearing companies, sharing-economy advocates are optimistic and believe the key to success lies in collaboration.
According to Airbnb, “The sharing economy is a new paradigm for people, but when we work together, leaders and community members around the world quickly see how Airbnb makes communities stronger.”
Some say issues around legality will become irrelevant as the peer-to-peer movement legitimizes and becomes part of the mainstream and its benefits to the economy are realized.
According to Karesh, “The sharing economy is seeing a massive transformation. In the next five years it will not be a new economy but will be part of the economy.” Concerning the travel industry, Wong says, “It expands the tourism market with regard to communities and sustainability. … It’s not displacing the old market but creating a new one.”
Do you participate in the sharing economy as a traveler or host? Have you tried any of these peer-to-peer sites? If so, tell us about your experience in the comments below.
(Photos: EatWith; HomeExchange; HomeExchange; RelayRides; EatWith; Feastly; Ashley Ludaescher/Vayable)
You Might Also Like:
- 10 Authentic Ways to Travel Like a Local
- 10 Summer Trips That Will Change Your Life
- 10 Trips That Will Make You a Better Person
We hand-pick everything we recommend and select items through testing and reviews. Some products are sent to us free of charge with no incentive to offer a favorable review. We offer our unbiased opinions and do not accept compensation to review products. All items are in stock and prices are accurate at the time of publication. If you buy something through our links, we may earn a commission.
Related
Top Fares From
Today's Top Travel Deals
Brought to you by ShermansTravel
Greenland: Luxe, All-Incl. 11-Nt Exploration Small-Ship...
Swan Hellenic
 cruise
$3289+
cruise
$3289+
Ohio: Daily Car Rentals from Cincinnati
85OFF.com
 Car Rental
$19+
Car Rental
$19+
Shop and Save with Country Inns...
Patricia Magaña
 Hotel & Lodging Deals
Hotel & Lodging Deals






